Brain implant sensor for neurotransmitters monitoring
This project aims the fabrication of a novel microarray probe for in vivo, real-time sensing of glutamate (GLU) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GLU and GABA are NTs that are essential for normal brain function, neuronal activity, information processing and plasticity, and network synchronization. The novel Si probe features four surface-functionalized platinum (Pt) ultramicroelectrodes (UMEs) for simultaneous amperometric detection of GLU and GABA, and a built-in microfluidic channel for the introduction of neurochemicals in the immediate vicinity of the UMEs.
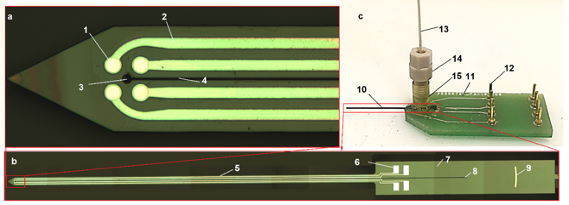
1 -Pt microelectrode (functionalized)
2 -SiNx-insulated Pt leads
3 -pore opening of microchannel
4 -microchannel sealed with SiNx
5 -probe shaft of length 1cm
6 -electrical connection pads for wire-bonding
7 -Si handling chip
8 -inlet pore opening of the microchannel
9 -guidance for microfluidic ferrule mounting;
10-Si-probe
11-custom PCB with Au leads
12-electrical connector pin
13-capillary tube
14-microfluidic connector
15-microfluidic ferrule glued onto the Si probe after wire bonding


